Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
Moreover in this study weak
2020-02-18
Moreover, in this study, weak expression of MT1 and MT2 was also detected in the oviduct muscular layers. Although there are no reports regarding the role of MT1 and MT2 in oviduct muscular layers, previous studies have demonstrated that melatonin plays an important role in the uterine contractility
-
Besides the assessment of toxicological effects
2020-02-17
Besides the assessment of toxicological effects immediately after exposure, we also studied the potential recovery of the exposed organisms, through the quantification of ChE activity at specific time intervals after placing organisms in clean test medium. Recovery from chemical challenge, in this c
-
To avoid the difficulty of the
2020-02-17
To avoid the difficulty of the nonsmooth constraints, a sequence of smooth problems by using smoothing functions have been progressively approximated this nonsmooth problem. To date, there have been many smoothing functions, such as perturbed Fischer–Burmeister (FB), Chen–Harker–Kanzow–Smale (CHKS),
-
We aim to apply the same technology to target
2020-02-17
We aim to apply the same technology to target other collagen-binding proteins using motifs from collagens that are specific for other receptors or matrix components. Previously, we synthesized THP libraries, called Toolkits, composed of an active guest sequence flanked by five GPP host triplets that
-
Sensory gating describes a filter mechanism protecting the c
2020-02-17

‘Sensory gating’ describes a filter mechanism protecting the central nervous system from sensory overload by inhibiting behaviorally irrelevant input (Boutros et al., 2004, 2008). This permits ARCA EGFP mRNA to a changing contextual environment (Fruhstorfer et al., 1970; Grunwald et al., 2003). Aud
-
br Transparency document br Results and Discussion
2020-02-17
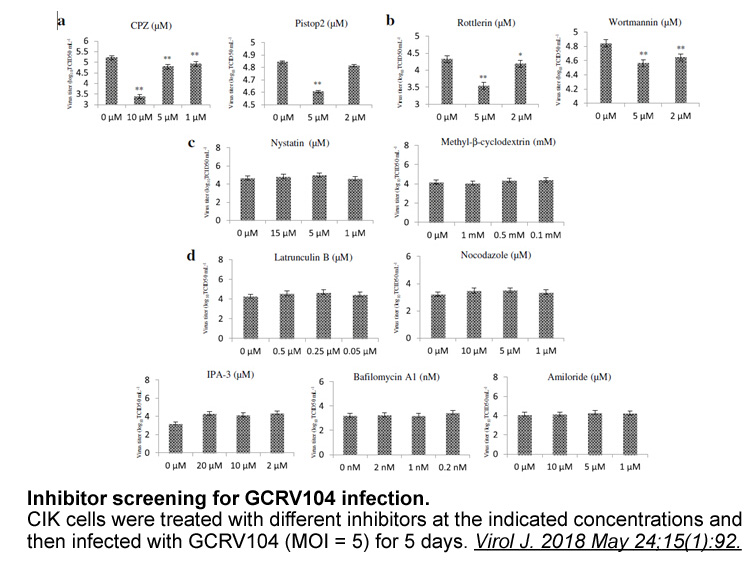
Transparency document Results and Discussion Experimental Procedures Acknowledgments The casein kinase 1 (CK1) family consists of at least seven different gene products, often referred to as isoforms (α, β, γ1, γ2, γ3, δ, ε, with splice forms described for CK1α, γ, and ε (reviewed in )
-
Adarotene mg br Discussion We are reporting
2020-02-17
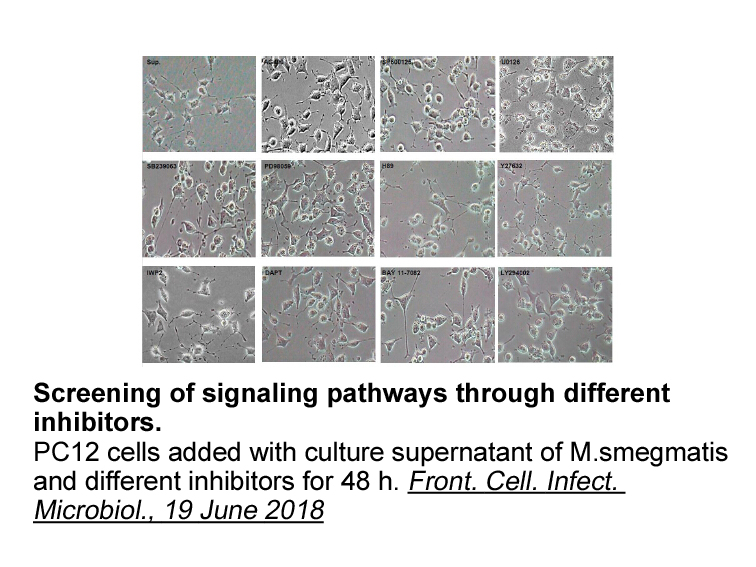
Discussion We are reporting a cryptic insertion of chromosome 22 material (EWS) to the long arm of chromosome 11 (11q24, FLI-1) recognizable by FISH in Adarotene mg exhibiting trisomy 8 as the sole cytogenetic anomaly. In ES and PNET tumors, trisomy 8 is the most common secondary abnormality [6]
-
br Role of ERK signaling in preventive and therapeutic poten
2020-02-17
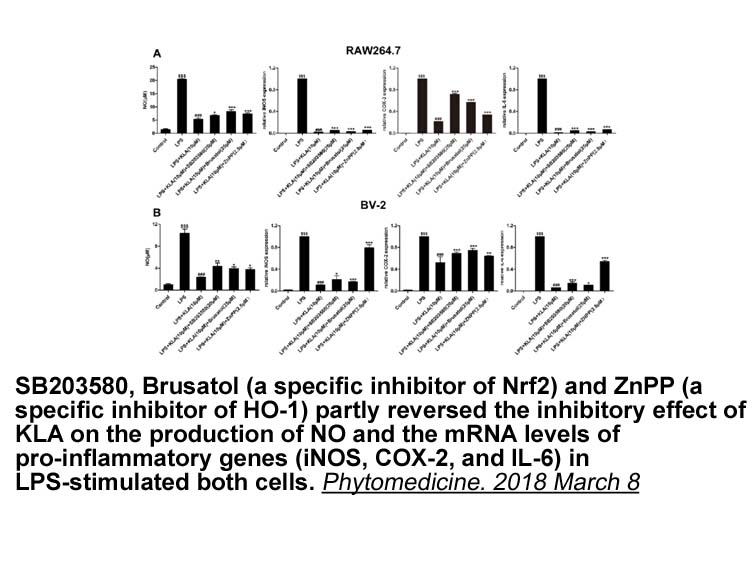
Role of ERK signaling in preventive and therapeutic potential of flavonoids in neurodegenerative diseases ERK is one of the main pharmacological targets of natural phenolic compounds and contributes to several therapeutic approaches including anti-atherogenic, anti-cancer, anti-colitis, anti-arth
-
Our approach including the characterization of
2020-02-15

Our approach, including the characterization of histone modifications in scarce NK subsets, allowed us to identify super-enhancers, which associate with genes endowing a given cell type with its unique identity (Hnisz et al., 2013). Especially intriguing were SEs with distinct activities in NK subse
-
Extracellular uridine can be transported across the cell
2020-02-15

Extracellular uridine can be transported across the cell membrane to enter the nucleotide salvage pathway. A colon cancer cell line supplemented with uridine was capable of growing normally in the presence of 1 μM brequinar (Peters et al., 1992). The supplemented uridine may be transported into the
-
br Materials and methods br Results The
2020-02-15
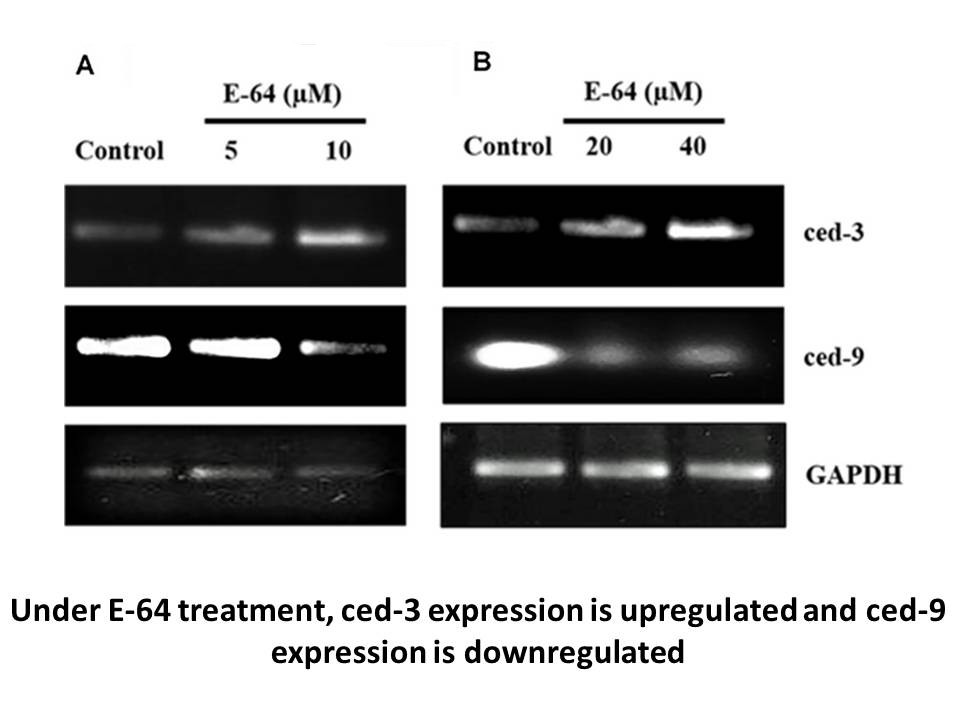
Materials and methods Results The BUN and creatinine levels in the saline-treated CRF group were found to be significantly higher than those in the sham-operated control rats treated with either montelukast or saline (pflunixin meglumine tissues, were found to be significantly higher in the s
-
Arsenic could cause apoptosis in both benign
2020-02-14
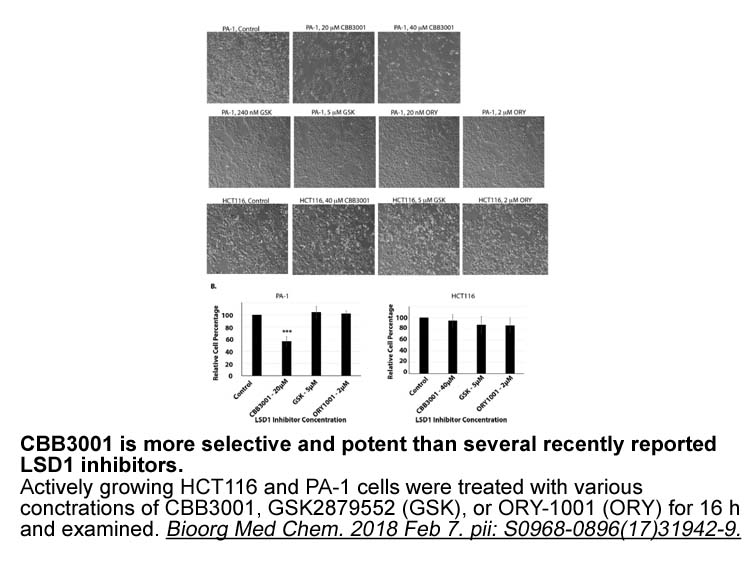
Arsenic could cause apoptosis in both benign and malignant cells (Akao et al., 2000, Gupta et al., 2003, Namgung and Xia, 2001). However, at present, little is known about the consequences of arsenic-treated urothelial cells in autophagy and expression of its related proteins. In addition, the alter
-
Dexamethasone DEX a potent synthetic glucocorticoid drug is
2020-02-14
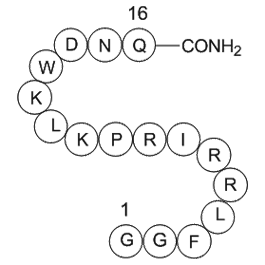
Dexamethasone (DEX), a potent synthetic glucocorticoid drug, is effective for treatment of a range of inflammatory and autoimmune conditions as well as the reduction of side effects associated with chemotherapy. On the Czech Republic pharmaceutical market, DEX is incorporated into eighteen drugs use
-
In summary in the present study we found
2020-02-14
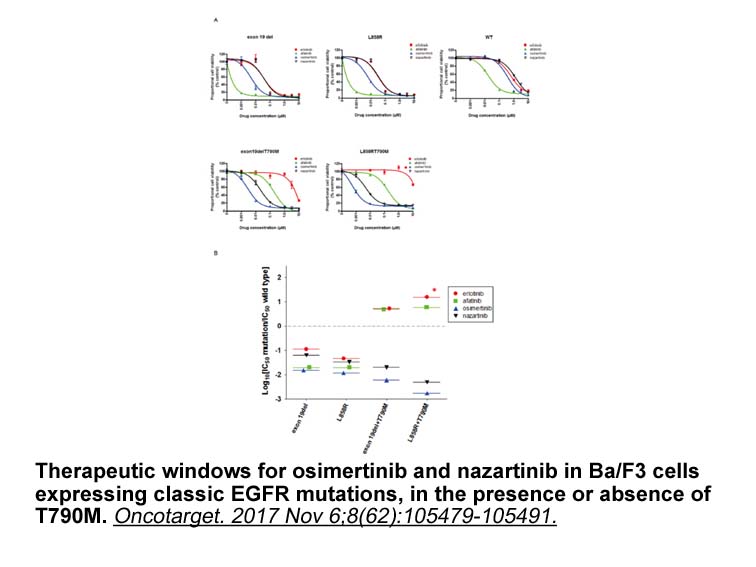
In summary, in the present study we found that CysLT1 receptor attenuates while CysLT2 receptor facilitates OGD-induced PC12 cell death as confirmed by receptor over-expression and antagonism. However, we cannot explain why their roles are distinct and why the cell size is increased in the CysLT2 re
-
CCT129202 Based on our studies presented above atipamezole c
2020-02-14
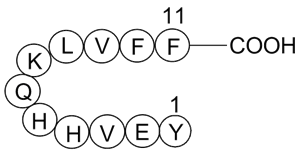
Based on our studies presented above, atipamezole can be used as a new in vitro and in vivo tool CCT129202 as a pan-CYP inhibitor for CYP mediated metabolism study. It carries many unique characteristics compared to ABT which is currently being widely used for this purpose. These new characteristic
16209 records 917/1081 page Previous Next First page 上5页 916917918919920 下5页 Last page